Blood sample: process, necessity and required instruments
Blood sampling is one of the most common medical procedures carried out in medical practices, clinics and laboratories. It is an essential part of the Diagnosis and prevention of diseases. By analyzing the blood taken, important information about the health of a patient can be obtained, such as blood count, blood sugar levels or markers for infections and other diseases.
When is a blood sample necessary?
Blood extraction is necessary in various medical situations:
- Diagnostic purposes: To determine and monitor diseases such as anemia, diabetes, infections, thyroid diseases and many others.
- Routine examinations: As part of preventive examinations to recognize and treat health problems at an early stage.
- Control of medication mirrors: To monitor the effect and dosage certain drugs, especially in chronic diseases.
- Preoperative studies: Before operations to assess the patient's general state of health and minimize risks.
Blood expiry expiry
Blood sampling is a standardized process that ensures that a sufficient amount of blood is removed for the necessary tests, while the risk of complications is minimized. Here is the exact expiry of a typical blood sample:
- Preparation of the patient: The patient is asked to expose his arm and go into a comfortable position. The arm is stretched out to facilitate access to the vein.
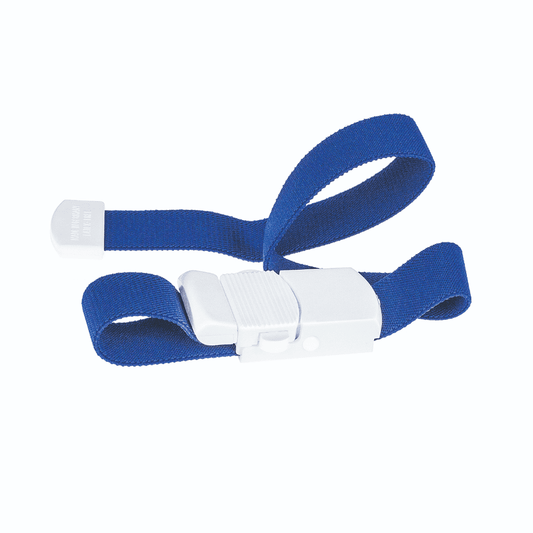
- Creation of the venous congestion: A Venous congestion is created about 10-15 cm above the puncture site on the upper arm to slow down the blood flow and let the vein emerge. This makes puncture easier.
- Disinfection of the puncture position: The skin at the puncture site is thoroughly with an alcoholic Disinfectant wiped off to minimize the risk of infection.
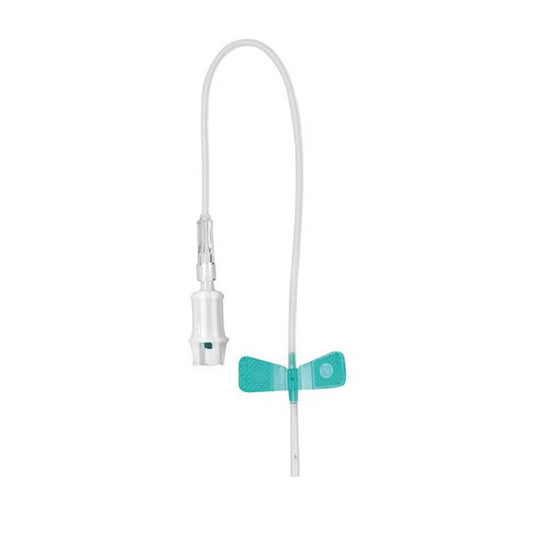
- Implementation of the puncture: One Blood withdrawal cannula is carefully inserted into the vein. The choice of Cannula depends on the amount of blood required and the thickness of the vein. The cannula is often connected to a special adapter that enables different blood withdrawal systems such as Monovettes or use vacuum tube.
- Blood absorption with monovettes or vacuum tube: As soon as the needle lies correctly in the vein, the corresponding tube (e.g. one Monovette) attached to the adapter. The monovette works similarly to a syringe: by pulling out the piston, the blood is sucked into the tube. Alternatively, vacuum tube can be used in which the blood automatically flows into the tube due to the vacuum generated.
- Solving the venous congestion: As soon as enough blood has been collected, the venous congestion is solved to restore normal blood flow.
- Distance of the cannula and aftercare: The cannula is carefully removed and the puncture site with a sterile swab or Pavement covered. The patient is asked to put pressure on the spot for a few minutes to prevent bleeding.
- Sample identification and shipping: The blood samples taken are carefully labeled and sent to the laboratory for the analysis.
Necessary instruments for blood sampling
A blood collection requires special instruments that ensure both the safety of the patient and the quality of the sample taken:
- tourniquet: A rubber band or blood pressure cuff that temporarily slows blood flow to make the vein protrude and make the puncture easier.
- Blood collection cannulas: Sterile needles available in different sizes to be used depending on the thickness of the vein and the amount of blood desired.
- Monovettes: Special blood collection systems that work like syringes and collect blood safely and in a controlled manner. They are available in different sizes and with different additives that are necessary for different tests.
- Vacuum tubes: These tubes are equipped with a negative pressure that automatically sucks in the blood as soon as the cannula is inserted into the vein and the tube is attached. They are also available in different versions, depending on the type of sample required (e.g. serum, plasma).
- Disinfectant and sterile swab: For cleaning the puncture site and caring for the puncture site after removal.
- Pavement or Association: To cover the puncture site after blood collection to prevent infection and stop bleeding.
Blood collection is a basic and important procedure in medicine that is used to diagnose and monitor numerous health conditions. The use of specialized instruments such as tourniquets, blood collection cannulas and monovettes ensures that the procedure is carried out safely and effectively. Understanding the different steps and tools required helps one better understand the process of blood collection and appreciate how crucial this simple procedure is to preventive health care.